A Nutrient-Dense Vegetable with Impressive Health Benefits
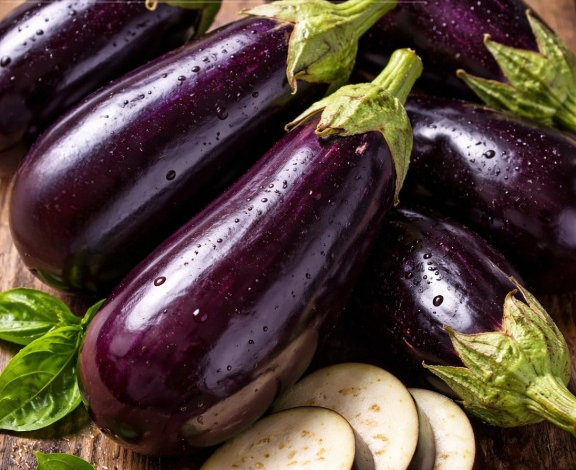

Eggplant — also called aubergine — is a staple of the Mediterranean diet and one of those foods that quietly does a lot for your body. It’s low in calories but packed with fiber, vitamins, minerals, and plant compounds that support overall health.
A single serving provides at least 5% of daily needs for:
Fiber
Copper
Manganese
Vitamin B6
Thiamine
It also contains potassium, vitamin C, and protective phytonutrients. Because it’s high in water and fiber, it fills you up without adding many calories — helpful for weight management.
Powerful Antioxidants in Eggplant
Its deep purple skin isn’t just pretty — it signals potent antioxidants, especially nasunin, an anthocyanin.
Key protective compounds include:
Anthocyanins (nasunin)
Lutein
Zeaxanthin
Chlorogenic acid
These compounds help neutralize free radicals that damage cells and accelerate aging.
Chlorogenic acid, in particular, has been studied for potential anti-cancer, antibacterial, antiviral, and heart-protective effects.
Health Benefits
1. Heart Health
Eggplant supports cardiovascular wellness thanks to fiber, potassium, and antioxidants.
Research links anthocyanins with:
Reduced inflammation
Lower blood pressure
Improved arterial flexibility
2. Cholesterol Regulation
About 2.4 g fiber per 96 g cooked eggplant helps:
Lower LDL (“bad”) cholesterol
Improve digestion
Support heart function
3. Cancer-Protection Support
Polyphenols and anthocyanins may:
Slow tumor blood vessel growth
Reduce inflammation
Block enzymes cancer cells use to spread
(Research is ongoing, but results are promising.)
4. Brain Function
Nasunin protects brain cell membranes from oxidative damage.
Associated benefits:
Better blood flow to the brain
Reduced neuroinflammation
Slower age-related cognitive decline
Memory protection
5. Weight Management
Low calories + high fiber = better satiety.
⚠️ Note: Eggplant absorbs oil easily when fried.
Healthier methods: roasting, grilling, steaming, or air-fying.
6. Eye Health
Lutein and zeaxanthin help:
Protect against macular degeneration
Reduce oxidative eye damage
Support long-term vision
Who Should Limit Eggplant?
1. Iron-deficiency anemia
Skin compounds can slightly reduce iron absorption.
2. Sensitive stomach
May cause discomfort if eaten in excess.
3. Weak digestion
Peeling and cooking thoroughly helps tolerance.
4. Kidney stones or kidney disease
Contains oxalates — consult a healthcare professional.
Bottom Line
Eggplant is a low-calorie, fiber-rich vegetable loaded with antioxidants that support heart, brain, digestive, and eye health.
For most people, it’s an excellent addition to a balanced diet — especially when cooked with minimal oil.
Nutritious, versatile, and satisfying, eggplant proves that some of the healthiest foods are also the simplest.