If You Notice a Lump on Your Neck, Back, or Behind Your Ear, It Could Mean…
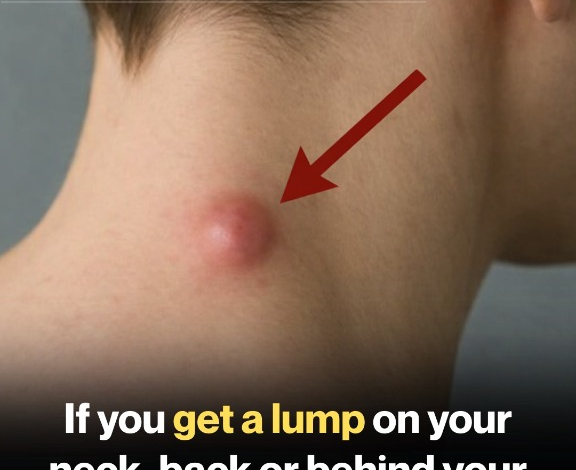
Discovering a lump on your neck, back, or behind your ear can be unsettling—especially if it seems to appear out of nowhere or feels different than anything you’ve noticed before. Although many lumps are harmless and temporary, some can point to an underlying health issue that shouldn’t be ignored.
Lumps can differ greatly in size, firmness, and cause. Some fade away on their own, while others remain the same or slowly increase in size. Knowing the possible reasons behind a lump can help you understand how to manage it and recognize when it’s time to seek medical advice.
For illustrative purposes only (Wikipedia)
This article breaks down the most common reasons lumps appear—particularly epidermoid cysts—along with their symptoms, possible at-home care, risks, and medical treatment options.
What Is an Epidermoid Cyst?
An epidermoid cyst is a very common, non-cancerous growth that forms just beneath the skin. These cysts usually grow slowly and can develop almost anywhere on the body, but they most often appear on the neck, back, face, or behind the ears.
They form when skin cells that are normally shed become trapped under the skin’s surface. Instead of shedding, these cells continue to multiply, creating a small sac filled with keratin—a thick protein also found in hair and nails.
In most cases, epidermoid cysts are painless and harmless. However, they can sometimes become irritated or infected, leading to redness, swelling, and discomfort.
Causes and Risk Factors
Epidermoid cysts may develop as a result of:
Blocked pores or hair follicles
Minor skin injuries or trauma
Ongoing skin conditions such as acne
Certain inherited conditions, including Gardner syndrome
Although anyone can develop an epidermoid cyst, they tend to occur more frequently in adults—especially men—than in children.
Symptoms and How Lumps Are Diagnosed
The most noticeable sign is usually a small, round bump beneath the skin. Common characteristics include:
A smooth or slightly firm feel
A skin-toned or pale color
No pain unless the cyst becomes inflamed or infected
If infection occurs, additional symptoms may include:
Redness and warmth around the area
Swelling or tenderness
Thick discharge with an unpleasant odor
Doctors typically diagnose epidermoid cysts through a physical exam. If the lump looks unusual or the diagnosis is uncertain, further tests may be recommended, such as:
Ultrasound or MRI scans to evaluate size and depth
A biopsy to rule out other conditions
Common Home Remedies People Try
Some individuals turn to home remedies to ease discomfort or inflammation caused by lumps or cysts. While these methods are not proven to eliminate cysts, they may provide temporary relief for mild symptoms.
Warm Compress
How to use: Apply a warm (not hot), damp cloth to the area for 10–15 minutes, three to four times daily.
Purpose: May help reduce swelling and promote drainage if a blocked gland is involved.
Apple Cider Vinegar
How to use: Dilute with equal parts water, apply briefly using a cotton ball, then rinse.
Purpose: Thought to have antibacterial properties, though it may irritate sensitive skin.
Tea Tree Oil
How to use: Dilute a few drops in a carrier oil and apply gently once or twice a day.
Purpose: Known for antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effects.
Turmeric Paste
How to use: Mix turmeric powder with water or coconut oil, apply for 30–60 minutes daily, then rinse.
Purpose: Contains curcumin, which may help reduce inflammation.
Aloe Vera Gel
How to use: Apply pure or fresh aloe vera gel directly to the area twice daily.
Purpose: Helps soothe irritation and supports skin healing.
Castor Oil
How to use: Apply with a clean cloth, cover with a warm compress, and leave on for 15–30 minutes each day.
Purpose: May help soften tissue and reduce inflammation.
⚠️ Important: Home remedies should never replace professional medical evaluation, especially if a lump is painful, growing, or persistent.
Caring for a Lump at Home
If a healthcare provider confirms that a lump is harmless, supportive care may include:
Keeping the area clean and dry
Avoiding squeezing, picking, or scratching
Using warm compresses to ease discomfort
Taking over-the-counter pain relievers if necessary
Seek medical attention immediately if signs of infection appear, such as increasing redness, swelling, warmth, or discharge.
Risks and Limits of At-Home Treatments
Trying to pop or drain a cyst on your own can cause:
Infection
Scarring
Worsening inflammation
Some natural remedies can also trigger skin irritation or allergic reactions. Discontinue use if you notice burning, redness, or itching.
When Should You See a Doctor?
Consult a healthcare professional if a lump:
Grows rapidly or changes shape or color
Becomes hard, painful, or immobile
Shows signs of infection
Is accompanied by fever, fatigue, or unexplained weight loss
Early medical evaluation helps ensure accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Medical Treatment Options for Epidermoid Cysts
Professional treatment may include:
Incision and drainage for inflamed cysts
Complete surgical removal to reduce recurrence
Antibiotics if an infection is present
These procedures are typically minor and performed under local anesthesia.
How to Lower the Risk of Future Cysts
While not all cysts can be prevented, good skin care habits may help:
Cleanse skin gently and regularly
Use non-comedogenic skincare products
Avoid unnecessary skin trauma
Resist the urge to squeeze or pick blemishes
Consult a dermatologist if cysts keep returning
Final Thoughts
Most lumps beneath the skin—especially epidermoid cysts—are not dangerous. Still, any lump that changes in size, becomes painful, or looks unusual deserves attention. When you’re unsure, seeking medical advice is the safest way to protect your health and gain peace of mind.



